 Serbia EN
Serbia EN Serbia EN
Serbia ENHugo Zwartkruis
Consultant Regulatory Change and Compliance , The Netherlands
Bram Zwagemakers
Senior Manager , The Netherlands
Digital
With the upcoming publication of the second wave of the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) policy standards, we’re taking a detailed look at one of its underlying pillars. But, before we do so, it’s important to provide some context.
Since the pandemic, the financial sector has become increasingly dependent on digital technologies provided by external service providers. This is making financial institutions more vulnerable to cyber-attacks and other disruptions. DORA is a piece of EU legislation that aims to promote the robustness and resilience of their operations, while at the same time fostering a sustainable digitalization of the financial sector.
DORA was adopted in December 2022 and entered into force on 16 January, 2023. Some Regulatory Technical Standards (RTS) are still under development so the contents of this article may be subject to change.
DORA applies to a wide range of financial institutions, including banks, investment firms, insurance companies, and payment service providers. DORA also applies to some non-financial institutions that are critical to the financial system. These institutions are known as critical third-party service providers (CTTPs). CCTPs are entities that provide essential services to financial institutions, such as cloud service providers, and data centers. These different types of financial institutions are now subject to harmonized standards on digital operational resilience.
One of DORA’s main pillars is to strengthen the digital operational resilience of the financial sector by standardizing how financial institutions identify, manage, and report major information and communication technology (ICT) incidents across EU member states and different sectors. This includes the ability to classify cyber threats that could cause the disruptions and the reporting thereof and allows competent supervisory authorities to adopt definitions and processes that are applied consistently across member states.
While established incident management processes exist within many mature financial institutions' risk management frameworks, DORA introduces new requirements for ICT-related incident management, classification, and reporting.
DORA imposes enhanced regulatory obligations for incident management that are significantly more onerous than those in existing regulations. With the level of detail in this new rule-based framework, financial institutions will have to fully re-establish how they deal with incidents. The visual below offers a more in-depth representation of DORA’s incident management process.
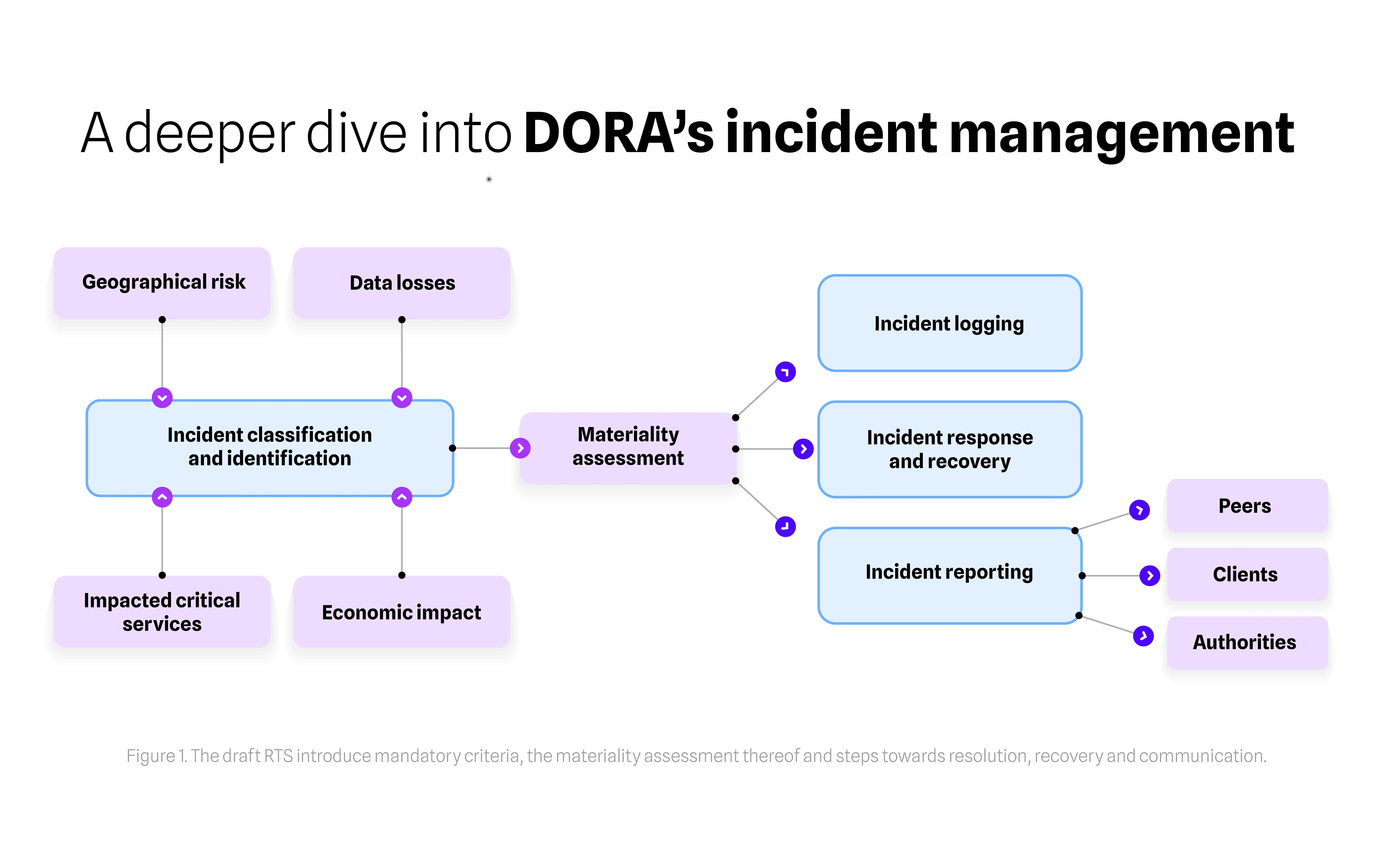
In preparation for DORA's incident management framework, several key recommendations have been outlined:
Synechron supports clients with these topics, through enhancing incident management. We conduct a thorough assessment, identify critical gaps, and create an implementation plan tailored to their characteristics.
In further technical standards the European Commission has urged for an eye to proportionality in applying incident classification criteria, steering financial institutions to look at incident reporting pragmatically. If the classification exercise leads to disproportionate incident reporting, they should adjust accordingly. At the same time financial institutions should also assess incidents qualitatively as cyber attacks or if numerous small interuptions may not meet materiality thresholds, they however can be indicative to serious or structural shortcomings in risk management.
Synechron's DORA experts combine regulatory expertise with project management and technological capabilities. With a focus on operational resilience, we turn regulatory complexity into structured compliance, ensuring seamless DORA integrations and fortified ICT frameworks. Whether it's crafting bespoke progress reports or revolutionizing your incident management with digital tooling, Synechron stands as your navigator in the ever-evolving landscape of digital operational resilience, transforming regulatory requirements into strategic advantages.